How is gold refined? The process is crucial for removing impurities and achieving high purity for jewelry, investment, and industrial use. Raw gold from mining or recycling contains metals like silver, copper, and lead. Refining eliminates these impurities, increasing its value and usability.
This article explores traditional and modern gold refining methods, comparing their efficiency, benefits, and drawbacks.
Traditional Gold Refining Methods
Early gold refining techniques relied on fire and chemical processes. While effective, these methods posed safety risks and had environmental concerns. Let’s explore three primary traditional methods.
Cupellation (Fire Refining)
Cupellation is an ancient refining method that uses high heat to extract gold from lead and other metals. Impure gold is placed in a porous cupel and heated in a furnace. As the temperature rises, lead, copper, and tin oxidize.
These impurities either vaporize or get absorbed by the cupel. In the end, pure gold remains. Cupellation can be highly precise, though the margin of error varies based on conditions.
Advantages:
- Simple and effective for removing lead and other base metals.
- No need for complex chemical treatments.
Disadvantages:
- Ineffective for refining gold with high silver content.
- Requires high temperatures and skilled handling.
Amalgamation (Mercury Method)
How is gold refined using the amalgamation method? Gold particles mix with mercury, forming an amalgam. When the amalgam is heated, mercury evaporates, leaving behind sponge gold. This method is simple, low-cost, and effective for high-grade ores.
This method extracts gold from ore containing 2-3 grams per ton. The process produces gold amalgam with 30% purity. However, mercury is highly toxic. Strict handling and environmental controls are required. Historically, some small-scale operations reported gold recovery rates of up to 70% using this method, though modern regulations restrict its use due to environmental concerns.
Advantages:
- Effective for capturing fine gold particles.
- Used in small-scale gold recovery.
Disadvantages:
- Mercury is highly toxic and poses health risks.
- Banned or restricted in many countries due to environmental concerns.
Acid Treatment
Acid refining dissolves gold impurities using nitric or hydrochloric acid, often with substitutes like MX3. Gold is melted into the shot, dissolved in acid, and then treated with urea to neutralize excess nitric acid.
A precipitant recovers pure gold, which is rinsed, dried, and melted. Testing ensures no gold loss. Platinum requires heated aqua regia for separation. Proper safety measures, ventilation, and filtration are essential for efficiency and safety in gold refining.
Advantages:
- Can achieve high-purity gold.
- Effective for removing base metals.
Disadvantages:
- Handling strong acids requires safety precautions.
- Not as efficient for bulk refining.
Modern Gold Refining Methods
Modern technology has improved how gold is refined, making the process more efficient and safer. Here are the most widely used modern methods.
Miller Process
The Miller process purifies gold using chlorine gas. The gas passes through molten bullion. It reacts with impurities like silver, forming chlorides. The chlorides float to the surface, where they are removed.
This method was developed by Francis Bowyer Miller in the 1860s and is used to efficiently refine gold with minimal loss. It became widely used in Australian mints, replacing older methods and making gold coins purer without high costs.
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient for large-scale refining.
- Removes most impurities effectively.
Disadvantages:
- Gold purity is limited to about 99.5%.
- Requires additional refining for ultra-pure gold.
Wohlwill Process
Gold is refined to 99.999% purity using the Wohlwill process and electrolysis. The method was invented by Emil Wohlwill in 1874. One hundred-ounce anodes of impure gold are cast and then dissolved in an electrolyte solution.
Thin cathode strips collect pure gold, while silver and other impurities settle at the bottom. Since the process takes about two days, followed by melting and casting, it is considered one of the most effective gold refining methods.
Advantages:
- Produces the highest purity of gold.
- Suitable for industrial and investment-grade gold.
Disadvantages:
- Slower and more expensive than the Miller process.
- Requires specialized equipment and controlled conditions.
Aqua Regia Method
Aqua regia, a 3:1 hydrochloric and nitric acid mixture, dissolves gold and some platinum group metals. This method has been used for over 1,000 years, forming tetrachloroaurate ions (AuCl₄⁻). It is best suited for gold with at least 60% purity. Silver content must be below 10-12% for efficiency.
Gold is dissolved as thin strips or grains, then selectively precipitated using reducing agents like sulfur dioxide. Industrial setups use polypropylene or glass digesters for controlled refining.
Advantages:
- Effective for refining high-purity gold.
- Used in laboratory and small-scale refining.
Disadvantages:
- Produces toxic fumes and requires proper ventilation.
- Acid disposal must be handled carefully.
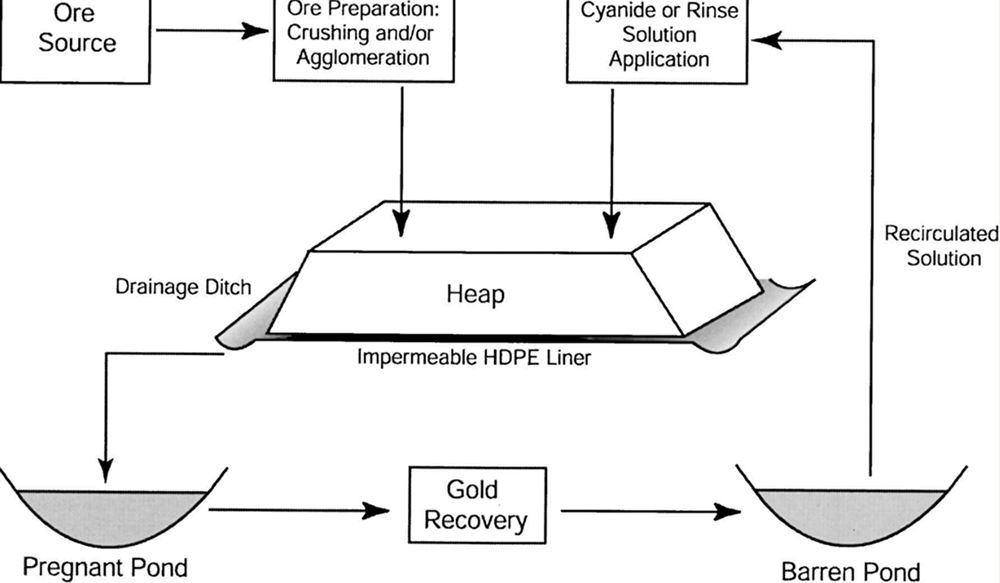
Cyanide Process (Gold Leaching)
Gold leaching dissolves gold using a cyanide solution, then recovers it through carbon-in-leach (CIL), carbon-in-pulp (CIP), or Merrill-Crowe methods. Reusing cyanide solutions cuts waste and makes gold recovery more sustainable.
Advantages:
- Efficient for processing low-grade ores.
- Widely used in large-scale mining operations.
Disadvantages:
- Cyanide is highly toxic and requires strict environmental controls.
- Not suitable for refining scrap gold.
For accurate gold analysis, a trusted lab helps you get the most value. Ledoux & Company offers expert precious metal assay services, ensuring precise measurement of gold purity and composition.
Whether refining for investment, jewelry, or industry, Ledoux offers top-tier testing to ensure you get the highest value. Get the best return and quality at every step.
Get Reliable Gold Refining Insights with Ledoux
Gold refining has come a long way, from fire-based methods to modern chemical and electrochemical processes. Knowing how gold is refined helps miners, jewelers, and investors pick the best method for purity and efficiency. While old techniques like cupellation and amalgamation still exist, advanced methods like Wohlwill and aqua regia offer higher purity and better safety.
For the best results, rely on Ledoux & Company for precise gold analysis and refining support!













